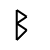
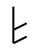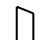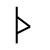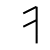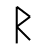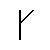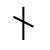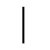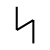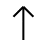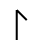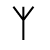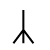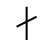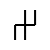Armanen Rune Set
The Armanen rune set, like other sets, has a difficult history to pin-point where and when it was established. Some will say that this set was originally developed by Guido List, while others will tell you that List followed the previous works of a scholar named Johannes Bureus. However, either way you look at it List’s work varies enough from previous scholar’s work to make the Armanen rune set one worth having a look at.
Gudio List (1848-1919) was the founder of a school of German rune work. The contributions to the study and preservation of the runes may be one of the reasons that we know as much about the runes as we do today. That’s not to say that all that List had taught was to be held as truth. In fact List claimed that his Armanen rune set was not only older than the Elder Futhark but that his set had laid the groundwork for the Elder Futhark as well as other rune sets.
It is said that the Armanen rune set came to List in a vision one day after he had become temporarily blind from an eye surgery. He envisioned 18 runes that were said to be the original rune set and the most ancient script for the Aryan race. However, if we look closely at the 18 runes we’ll notice that List simply took various Scandinavian rune sets, used from those sets various rune staves and then added 2 more to get a total of 18 rune staves for his set – which incidentally is the number of runes talked about in the Hávamál (Sayings of the High One – Part of the Elder Edda).
As far as the divinatory meanings for List’s runes we can see a close connection to the meanings of the Younger Futhork. However, with List’s set there are different meanings for daemoniums (reversed runes) as well as different names1. The use of this set among Germans and people in German speaking countries seems to be very widespread. However, since this set has ties to Socialist German, the Nazi party and in some aspects even to Hitler, we see this set being used less by modern day rune casters.
Armanen Runes – Rune Meanings
After an eye operation Guido List claimed to have had a vision where he saw the “original” set of runes. He claimed that these runes were the runes that all other rune-rows were based on. Having 18 runes in his set, he identified each of his runes with one of the 18 spells in the Havamal1 in the Elder Edda. However, there was no evidence to support his claim.
Sound: “f”
Stands for: Primal Fire
Casting meaning: Symbolically this rune represents the power of spirit and change as well as the power of creativity.
Sound: “u”
Stands for: Resurrection
Casting meaning: Ur is a physician’s rune and represents resurrection, eternity, and continuity.
Sound: “th”
Stands for: Lightning and Thunder
Casting meaning: The rune represents the thunderbolt, but symbolically it stands for targeting goals, activity and the phallus.
Sound: “o” as in “cold”
Stands for: Mouth
Casting meaning: Os represents the spiritual power that is gained through speech. It is the breath of the world, its voice. It also signifies the strength that a person needs to rise up in power.
Sound: “r”
Stands for: Ritual (or Primal Laws)
Casting meaning: This rune represents the orderliness in the world, the ritual, primal law and things that are done correctly. It also stands for cynical events and rescue from an enemy.
Sound: “k”
Stands for: World Tree
Casting meaning: List’s version of this rune was simply for it to represent the world tree. However, more modern versions of this rune say that it stands for power, generation, ability and artfulness.
Sound: “h”
Stands for: Hail (not positive)
Casting meaning: Due to its shape Hagal is sometimes called the Mother rune and is said that all other runes derive from its shape. It is a rune of enclosure but contains a potential for growth.
Sound: “n”
Stands for: Necessity of fate
Casting meaning: This rune can be taken as the same idea as the Hindu concept of karma. What is done in this lifetime will determine our future existence.
Sound: “i” as in “piece”
Stands for: Ego
Casting meaning: Just like our ego, this rune is one that is used to control ourselves. It represents the personal power of control, obedience and our compelling will.
Sound: “a” as in “aah”
Stands for: Leadership
Casting meaning: Modern meanings of this rune are of beauty, fame, intelligence and virtue. List’s version of this rune has it representing sunlight that washes away darkness as well as having it denote nobility and leadership.
Sound: “s”
Stands for: Sun Power
Casting meaning: Like Ar this rune represents the power of the sun. The difference is that Sig is the power of the sun whereas Ar is the power that the light of the sun contains. It is also a rune of success and victory.
Sound: “t”
Stands for: Rebirth of the Sun God
Casting meaning: Tyr is a rune that has the power to make situations turn completely around. A rune of wisdom, spiritual understanding, and the power of generation.
Sound: “b”
Stands for: Birth
Casting meaning: This rune represents birth, but in a sense of the birth of the future life that is preordained for us. Modern versions of this rune say it stands for the power of becoming as well as the power of creativity found in song.
Sound: “l”
Stands for: Örlog (Primal Law)
Casting meaning: List said this rune stood for the concepts of defeat and the laws of nature. Today modern versions have this rune denoting life, water and primal law.
Sound: “m”
Stands for: Man (as in human, not gender)
Casting meaning: The second mother rune of this set, Man was used in Armanen tradition to represent birth. Modern versions say it stands for health, increase, maleness and man (gender this time).
Sound: “y” as in “tiny”
Stands for: Bow (or Rainbow)
Casting meaning: Modern interpreters see this as a female rune, the night, death and instinct. List said it denoted anger, falsehood, error and the oppositions found in man (as in human not gender).
Sound: “e” as in “every”
Stands for: Duality (or possibly even Horse)
Casting meaning: The rune Eh is said to symbolize duality where a pair is bound by primal law, love, trust and marriage.
Sound: “g”
Stands for: Gift of life
Casting meaning: This rune represents the giver of life and both the giver and the gift of life itself. It is also the cosmic consciousness and the divine principle.
Odin Discovers the Runes
The Elder Edda is a book of mythological stories of the Norse gods and goddesses and it is in here where we first see Odin learn about the runes. A story called Havamal1 or “Sayings of the High One2” tells us just how Odin first learned the runes.
Odin said:
I know that I hung on a high windy tree
for nine long nights;
pierced by a spear -Odin’s pledge-
given myself to myself.
No one can tell about that tree,
from what deep roots it rises.They brought me no bread, no horn to drink from,
I gazed toward the ground.
Crying aloud, I caught up the runes;
finally I fell.
We see that Odin, in a shaman-like self-sacrificing ritual, deprives himself of food and drink as he hangs upside down on a tree. In some translations we are told that this tree is Yggdrasil, the Norse World Tree. As the days drag out longer and longer for him, nine nights pass and it is then when Odin sees the shapes of the runes. Crying out, he catches up the runes and falls from the tree.
The poem goes on talking about the runes and how Odin knows how to carve them for magickal uses. There are a total of eighteen runes that are listed but we never are told the names nor hinted at what they may look like. However if you believe the stories and tales of Guido List then you would tend to accept the Armanen Runes to be the runes that Odin discovered. Of course there is no evidence to even come close to supporting List’s claim as his rune set being the very first and original rune set.
If you are looking for the section in the Hávamál where it talks about Odin and the runes, it starts on the 138th stanza in the poem. Or if your poem doesn’t tell you the stanza number look for the section “The Lay of Loaddfafnir” (which starts on the 111th stanza). Skim a little ahead and you should see it.
Rune Sets
There are many different versions or sets of runes that you will encounter as you read more about the runes. This is largely due to the history, travel and adaptation of the runes by different societies and cultures as they traveled around Europe. History tells us that the runes moved from society to society by the means of traders, travelers and warriors. A person may encounter and learn the runes from one society and then carry that knowledge to a new society through their travels. Since each society may have different phonetic sounds in their vocabulary the runes would take on new sounds, forms and meanings. For the most part you’ll see that the meanings and sounds didn’t change all that much. Similarities can be found between many sets. Of course there are times when you see that one rune set may be expanded or shortened to fit the needs of a specific society.
But what makes one set different from another set? Is it simply their shapes, meanings and sounds? Or can it be something deeper than that? From here on we’ll examine a few of the different rune sets and see what makes one different from the other. Click on the links to learn more about them.
Anglo-Saxon and Frisian Rune Sets – Expanded versions of the Elder Futhark rune set totaling 28 runes staves for the Frisian runes and 29 staves for the Anglo-Saxon set.
Armanen Rune Set – An 18 rune stave set created by Guido List. List claimed that this set was the “original rune set.”
Elder Futhark Rune Set – Also known as the German or Viking rune set, the Elder futhark set contains 24 rune staves.
Gothic Rune Set – This rune set of 25 staves was adapted from the Elder Futhark by a 4th century bishop for the use of writing Christian material.
Medieval Runes of Healing and Magick Set – These 8 runes were never really used for writing but were mainly associated with gods and goddesses that were worshiped in secret during Christian times.
Northumbrian Rune Set – This 33 rune stave collection was an extension of the Anglo-Saxon rune set adding 4 more runes to the already 29 rune set.
Younger Futhork Rune Set – Around the 7th or 8th century the Elder futhark rune set was shortened to 16 runes to form two new sets collectively known as the Younger futhork.
Rune Meanings
If you’ve had time to look at the different type of rune sets then you may be curious about is just what those runes stand for. As the runes were developed and as they transformed over time they came to stand for more than just sounds. They held magickal properties to people who used the runes for casting. They were still being used for writing so they held a phonetic sound as well. The name of each rune held a certain meaning and could stand for an item or an idea. For each different set below you will get to see an image of each rune, the phonetic value, what the rune stood for and also it’s meaning for casting purposes.
Anglo-Saxon and Frisian Runes – consists of the Elder Futhark Runes plus 5 more runes
Armanen Runes – similar to other runes in Scandinavia but were created by Guido List (1848-1919)
Elder Futhark Runes – sometimes called the German or Viking Futhark
Gothic Runes – the type of runes that are found on the Kylver Stone
Medieval Runes of Healing and Magick – 8 runes that were not used for writing but for magickal and healing purposes during the Middle Ages
Northumbrian Runes – consists of the Anglo-Saxon Runes plus 4 more runes
Younger Futhork Runes – includes the Danish and Swedish-Norse Futhark
It’s important to note that the names of the runes that you will find on other sites and in books may be different than the ones that you see on the pages for this site. For example the Elder Futhark rune “Kenaz” has at least five different names (or spellings) that I can think of off the top of my head. What I have done here is to use the names which I have used in my runic journal since I started it. You may also find that the images in a few books or other sites may be a little different as well. I took the most common images that I found in all of my rune books and used those in hopes that if you further your study on the runes that you may encounter the images I have used.
Sets in bold will be covered here when I get the time.